Understanding Construction Foundations
Pakistan’s construction landscape is evolving, offering a choice between traditional and green building methods. Traditional construction relies heavily on standard materials readily available in the market. For instance, cement prices range from Rs. 1,390 to Rs. 1,440 per 50kg bag, with premium brands like Bestway and DG Khan priced consistently around Rs. 1,420-1,430. Steel reinforcement, crucial for structural integrity, varies between Rs. 226-254 per kg depending on grade and location, with branded options commanding higher prices in major cities. Green housing, in contrast, incorporates sustainable materials and innovative construction techniques, providing a modern alternative to traditional methods.
Material Dynamics and Costs
Traditional construction employs A-class bricks costing Rs. 17,000 per thousand, while machine-made alternatives range from Rs. 14,000 to Rs. 18,000. Sand, a fundamental component, currently costs Rs. 44 per cubic foot, translating to Rs. 44,000 per damper (1,000 cubic feet). Labor costs for conventional construction average between Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 2,000 per square foot for basic work. On the other hand, green housing leverages fiber cement panels priced at Rs. 155 per square foot, with installation costs ranging from Rs. 150 to Rs. 300 per square foot. This approach not only streamlines construction but also reduces material wastage and labor dependency.
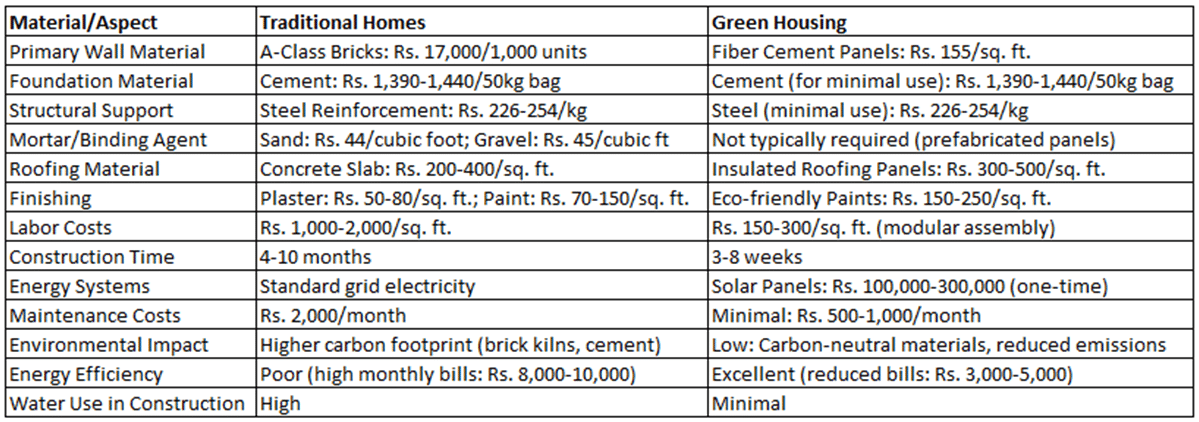
Comprehensive Comparison Table
Here’s a detailed comparison of the materials and aspects involved in constructing traditional homes versus green housing:
Efficiency and Performance
Efficiency sets green housing apart. Traditional homes typically incur monthly electricity bills of Rs. 8,000 to Rs. 10,000 and maintenance costs of Rs. 2,000 monthly. The construction timeline for conventional homes spans four to ten months, significantly affecting project costs and time. Green housing’s modular design and efficient assembly system drastically reduce construction time, often completing projects in weeks. Moreover, superior energy performance translates into substantial monthly savings. ModulusTech reports significant CO2 emissions reductions through its green housing technology, emphasizing the environmental benefits.
Comprehensive Cost Analysis
A detailed financial comparison for a 120 square yard house (1,080 square feet) reveals the true cost dynamics between traditional and green construction methods. Traditional construction requires an initial investment of approximately Rs. 6.44 million, including Rs. 4.82 million in construction costs at Rs. 4,465 per square foot and Rs. 1.62 million in labor, with annual running costs of Rs. 132,000 combining electricity and maintenance. In contrast, green housing totals Rs. 5.10 million initially (Rs. 4.86 million for construction at Rs. 4,500 per square foot plus Rs. 243,000 for installation), while annual operational costs amount to just Rs. 60,000, demonstrating significant long-term savings through reduced electricity consumption and maintenance needs.
Long-Term Value Proposition
While traditional construction materials might seem less expensive initially, the long-term cost analysis reveals a different picture. Green housing delivers value through multiple channels. Energy efficiency significantly reduces monthly electricity bills, with families saving up to Rs. 5,000 monthly. The minimal maintenance requirements substantially lower upkeep costs, while faster construction timelines reduce project expenses. These combined savings help offset the initial investment within just a few years.
Construction Technology and Standards
Green housing’s advanced technology integrates several cutting-edge features into a comprehensive building solution. The modular customization allows homes to be tailored to individual needs while maintaining carbon-neutral operations. Strict safety compliance ensures fire and earthquake resistance, while off-grid capabilities provide autonomous energy solutions. The innovative flat-packed, relocatable design adds flexibility, and the easy DIY assembly approach makes these homes accessible to a broader audience.
Global Leadership in Green Housing
The global green housing landscape is led by pioneering nations and their innovative projects. Germany headlines with the Frankfurt PassivHaus development, featuring over 300 certified energy-efficient homes consuming 90% less energy than conventional buildings. Singapore’s Punggol Eco-Town demonstrates large-scale sustainability with 25,000 green-certified residential units. Denmark’s Ørestad district in Copenhagen showcases the ‘8 House’ project, a 61,000 square meter mixed-use development achieving 85% energy efficiency. The UAE’s Masdar City leads desert sustainability with its residential quarters reducing energy consumption by 45%. Sweden’s Stockholm Royal Seaport stands out with 12,000 climate-positive homes, targeting fossil-fuel-free living by 2030. These successful implementations provide valuable blueprints for Pakistan’s sustainable construction future.
Future Outlook
As Pakistan’s construction sector advances, homeowners are increasingly prioritizing long-term value over initial costs. Green housing stands out as a sustainable and practical solution to modern housing needs. By integrating energy-efficient materials and innovative construction techniques, green homes offer a clear path to reducing environmental impact while enhancing financial savings.
Call to Action
The choice between traditional and green housing ultimately depends on your priorities. If you value energy efficiency, faster construction, and environmental sustainability, consider exploring green housing options today. For a better future, let’s build homes that not only shelter but also sustain.
